Key Points
- Disney’s performance will improve significantly as its cost-cutting and optimization strategies toward profitability will finally make Disney+ profitable by 2024, and its cost-cutting strategies for the DMED segment are within Disney’s range of control.
- The company’s net income margin is far from its 2019 level of approximately 16%, and it even bottomed at -4,34% in 2020, from where it has recovered to 3,80% at the end of Fiscal Year 2022.
- The implementation of Disney’s ad-supported tier on its Disney+ platform and global audience reach will provide a long-term boost to the company’s revenue from advertising across the globe.
- However, It is still uncertain how the ESPN and HULU operating segments will play out in the company’s organizational change toward profitability as their performance has added more pressure on Disney’s profitability.
Introduction
Disney stock price has experienced a significant downfall of 52% from its all-time high price of $197 back in March 2021 due to the slowing revenue on advertising that the industry as a whole is experiencing and the increase in programming and production costs, as well as some political pressure and Disney’s strategic change focused on its direct-to-consumer services which along with other shortfalls that we will discuss later on this article, have caused the net income margin to fall drastically to 3.80% for the FY 2022. The moat and magic image of Disney seems to have faded since 2020. So, can Disney come back to its pre-pandemic levels of profitability?
Disney Business Overview
The House of Mouse has a wide portfolio of products and services offered worldwide through its Media and Entertainment Distribution and the experiences offered through Disney Parks and Resorts, its cruise Line, and the licensing of Disney’s trade names for which they generate revenue through the royalties paid by manufacturers, game developers, publishers and retailers across the globe to use the trade names, characters and visuals of Disney.
Disney leverages its magic-like content production capabilities to distribute its well-known movies such as Toy Story, Dumbo, and Avatar just to name a few. They distribute those movies in theaters, which later get to be available on Disney+ or its linear network channels, and then they get to use those characters and trade names to create attractions in their parks, sell products directly to their customers, and also receive royalties when others use Disney’s characters or Intellectual Property on their merchandise.
Disney’s Financials and Business Analysis:
Disney Media and Entertainment Distribution (DMED) Segment:
This segment is comprised of the sub-segments Linear networks, Direct-to-Consumer and Content Sales/Licensing, and Others, which constitute 64% of Disney’s total revenue as of the 2Q earnings reported, and it experienced an increase of 3% in Q2 2023 in comparison with the same quarter in 2022, which was mainly driven by the increase in the Direct-to-Consumer segment. However, in Q2 2023, the operating income decreased to $ 1,119 million from the 1,944 million reported in Q2 2022, this represents a massive decrease of 42%. Let’s see the performance breakdown of each one of the sub-segments on the DMED segment.
Linear Networks:
For the second quarter that ended April 2023, the revenue from Linear Networks decreased 7% to $ 6.6 Billion in comparison with Q2 2022. This was mainly due to higher costs of production and programming on its television channels and broadcasting. The revenue from domestic channels decreased by 4% and the International Channels decreased by 18%, mainly due to an unfavorable foreign exchange impact.
The operating income for Linear Networks’ domestic channels decreased 33% to $1.6 billion due to higher sports programming and production costs and lower affiliate and advertising revenue. For the international channels, operating profit decreased 65% to $85 million due to lower advertising revenue caused by declining impressions, rates, and an unfavorable foreign exchange impact.
Direct-to-Consumer:
Disney+ is the key growth driver of this segment, and it is even expected to replace the revenue and profitability of Linear Networks in the long term. The company has seen astonishing growth on the Disney+ streaming platform launched in 2019, in almost a year, ending on October 3, 2020, Disney+ achieved 73.7 Million paid subscribers, and for Q2 2023, the company had 157.8 million on its combo Disney+ Hotstar. almost a 114% growth from its launch period, not bad at all. Although in the recent Q2, the number of paid subscribers decreased by 2% from the previous quarter on December 31, 2022, the average monthly revenue per paid subscriber increased to $ 7.14 from the $5.95 reporter in Q1 2023.
Besides the Disney+ platform, the ESPN+ paid subscribers increased by 2% to 25.3 million in comparison with the 24.9 Million reported in Q1, 2023. ESPN+ paid subscribers have achieved a compounded annual growth rate of 34% since the Q2 of 2020. And Disney’s Hulu platform has achieved a CAGR of 9% for the same period. The overall growth for the Direct-to-Consumer sub-segment reflects the quality of Disney’s movies and content, as well as its share in its customer’s minds, which is hard to be replaced the other competitors in the streaming industry.
The operating loss for Disney’s DTC services decreased by 26 % to $ 659 million. this reflects Disney’s focus and progress toward reaching profitability on its Disney+ platform. According to the comments from Disney’s CEO Bob Iger on the Q2 EarninsEarnings Call Transcription for Fiscal Year 2023, the strategic direction for the company relies on optimizing profitability through a cost reduction of $5.5 billion that will come mainly from content expenditure and SG&A cost reductions, which will mostly come starting 2024 and leading into 2025 since Disney has already committed to the content production for 2023.
Content Sales/Licensing and Other:
This sub-segment comprises Disney’s theatrical distribution and its content license to third-party television networks and stations. For Q2 2023, the revenue in the segment increased by 18% in comparison with the same quarter of the previous year. This increase was mainly driven by the success of Avatar: The Way of the Water, which was launched in the first part of 2023.
The operating results for this segment decreased from an income of $16 million to a loss of $50 million. This was mainly due to a decrease in sales volumes of film content and the change in Disney’s strategic focus on distributing its content through its DTC platforms and relying less on licensing its content to third parties.
Disney Parks, Experiences, and Products (DPEP) Segment:
The DPEP segment represents 36% of Disney’s revenues and this segment experienced a 17% increase in Q2 2023, and the operating income increased 23% to $2.2 billion, these improvements were mostly due to the recovery of Disney’s international and domestic parks and experiences businesses that were impacted due the Covid-19 Pandemic. For the Q2 FY 2023, the DPEP revenues were 8% higher than the pre-pandemic levels in 2019. To some extent, it was expected that this segment will improve as the Shanghai Disney Resort and Hong Kong Disneyland Resort saw their attendance increase, and the Disney Cruise Line aslo achieved an increase in passenger cruise days including the addition of the Disney Wish ship, which was launched in 2022.
As the DPEP segment revenue surge from its pre-pandemic levels, its growth will likely diminish as higher inflation costs will weigh on the consumer’s wallet at a moment when Disney’s customers are not very happy about the increase not only on the Disney park tickets but in all the products and services offered as things like food and merchandise have increased higher than inflation.
Speaking at a media conference in New York City On May 2023 (via Deadline), Disney’s CFO Christine McCarthy commented on the booming of DPEP and the public perception of higher admission costs and its sustainability, to what she said “We are in an inflationary environment. We are very aware of that, as inflation impacts everybody’s life” but then she touched on the profits from “experiential” food and beverage products related to theme parks and resorts, saying that the prices on these “experiential” products are not cheap but it reflects people’s choice to spend their money on. Although, her perspective on pricing reflects the fundamental principle of offer and demand, in some cases, Disney has increased its prices too far away from its once-loved and loyal middle-class segment.
These points are a real concern for the future growth of DPEP as there is a limit to what people will be willing to pay for Disney’s experiences, but we need to acknowledge as well that this is a broad issue for many of the companies, and the determinant factor will be how they respond to these higher costs without losing their customers and profitability even if their pricing power in the past has allowed them to stretch their prices constantly.
As we have seen in this segment breakdown analysis, Disney’s operating income for the DMED segment decreased by 42% for Q2 2023, and the operating income for DPEP increased by 23%. For this quarter Disney’s Net income increased 92,65% to 2,123 from the $1,102 net income reported on the Quarter Ended April 2, 2022. Most of these improvements were due to the reductions of cost and expenses that we have discussed previously.
However, Disney’s net income margin is far from its 2019 level of approximately 16%, and it even bottomed at -4,34% in 2020, from where it has recovered to 3,80% at the end of Fiscal Year 2022. We consider the profitability and net income of Disney will improve significantly as its cost-cutting and optimization strategies towards profitability are completely within the control of the Disney, and its dominance in the content industry will allow them to reduce the production of new films and digital content, and focus on producing the high-quality content that Disney’s viewers will value the most. So, Disney’s task remains solely on aligning the offer with the demand without losing a significant amount of paid subscribers.
Liquidity Ratio
When it comes to financial stability, Disney could be challenged as their liquidity ratio is 1.0 and the company does not have many resources to cover any unexpected charges or conditions that will affect the company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. And, in a highly uncertain environment that is an important risk to consider. Although Disney’s liquidity ratio has been pretty constant over the past 10 years with an average liquidity ratio of 1.05, they had not experienced a shrink in profit as they saw in 2020, and with interest rates going higher, Disney’s financial stability could get hurt significantly.
Debt to Shareholders’ Equity Ratio:
With a 1.0 Debt to Shareholder’s Equity Ratio, there is a significant amount of debt being used for Disnye’s operations. Usually, companies with great business economics have a ratio lower than 0.7 adjusting for the earnings used for stock buybacks, but for Disney, that is not the case, as we will see in the Shares outstanding. Moreover, Disney and Comcast signed a deal in 2019 that allowed Disney the option to acquire Comcas’s 33% stake in Hulu. This deal will come DUE in 2024, and it will certainly weigh on Disney’s leverage.
Disney’s Shares Outstanding
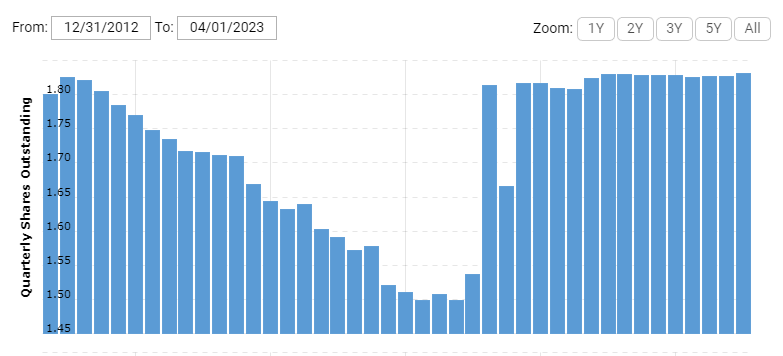
Over the past 10 years, Disney’s shares outstanding have remained almost flat as we can see in the chart above, Disney’s shares outstanding increased in 2019 as Disney financed 21st Century Fox with approximately $35.7 billion in cash and issued 343 million new shares to 21st Century Fox shareholders as per the Amended Acquisition Agreement. It is still unclear when Disney will re-start its share repurchase program due to the company’s tight financial condition and deteriorated free cash flow.
Disney’s Strengths and Growth Opportunities
Disney streaming business Disney+ and its different platforms are key drivers for the company’s future growth and performance. They have invested heavily in building the streaming platform and attracting subscribers, and they have seen spectacular results in terms of paid subscribers, as they have now 157.8 million paid subscribers in just over 3 years. The only aspect missing from this picture is profitability. Disney’s streaming business is still not generating free cash flow.
However, Disney’s path toward profitability is starting to unfold as its reduction of $ 5.5 billion in SG&A and optimization of content spending has shown progress on the company’s net income. Its organizational change to optimize capital allocation and marketing efforts on its films, especially in those markets where there is significant revenue potential, and its focus on reducing its efforts in those markets that have yield poor profit results, will strenght Disney’s competitive advantage and pricing flexibility to turn Disney+ into a profitable streaming business.
Another key opportunity for Disney, which was mentioned on the Q2 earnings call, is the launch of an ad-supported tier on Disney+. This has been already implemented in the US and Disney is expecting to extend the ad tier program in Europe by the end of 2023. This will provide a long-term boost in the company’s revenue from advertising as they continue to implement Disney+ with an advertising option to markets outside of the US.
Additionally, Disney’s ability to create value from its high-quality content production capabilities is remarkable. Disney can distribute its content through the theaters and then release the same content/films on Disney+ while reaching completely different audiences, and the same approach can be applied to the linear networks where they can show a movie on the Disney channel, or its ABC channel and then release it on Disney+ as well. And it does not ends there since Disney can use those films and its IP protected characters to create experiences through their theme parks, resorts, cruise lines, and products sold directly or through third parties. And this potential profitability from one piece of content is what makes Disney’s “IP” business model so valuable over the long term.
Disney’s Concerns and Risks
Although, Disney’s business model represents a strong competitive advantage for the company. The current market environment is not promising for most of the companies in the industry, and given Disney’s vulnerable financial condition and the reduction of customer’s spending on discretionary items, Disney could see a significant decline in its DPEP and DMED segments in the short term as the company struggles to find a sustainable balance between customer demand and Disney’s pricing on its products and services, which have experienced a steep price increase that in some areas have even outpaced inflation costs.
There are also risks in the political environment for Disney as its controversial involvement in certain social aspects, has led to a tight pressure from Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis in the company that could impact Disney’s Ready Creek Improvement District functionality.
Additionally, there is a well-based uncertainty regarding the profitability of Disney’s ESPN and HULU as these two business units belong to highly competitive markets, and it will be much more difficult for Disney to drive the company’s profitability through these business units as they are not as differentiated and don’t provide the same profitability as Disney’s core brands such as Pixar, Marvel, and Lucasfilm.
Disney’s Stock Valuation and Conclusion
Disney (NYSE: DIS) stock is currently trading at $ 93.14 per share with a P/E ratio (TTM) of 41.77 and a Price-to-Free-Cashflow of 31 using its 10-year average free cash flow remaining of $ 5.5 billion. Disney has been challenged by the Covid-19 Pandemic and the highly competitive streaming industry, but its value and moat remain clear and stable for the long term. However, at the current price, we consider Disney to be slightly overvalued as it will take a while for Disney to replace the decreasing value from the linear networks with the growing streaming services and platforms, and come back to its profitability levels from 2019.
Considering Disney executes properly its profitability measures and achieves a 12% net income margin over the next 10 years, with an average annual revenue growth of 5,5%. Our target price for Disney falls between the range of $70-75 per share for an expected 12% return, not very far from the current price, and considering the volatility and uncertainty spread in the market, we could see Disney stock selling at a more reasonable price.
Disclaimer
The information in this article and on our website does not constitute financial advice, investment advice, trading advice, or an offer to buy or sell any currency, product, or financial instrument. All information found here is purely for informational and educational purposes. You should not treat any opinion expressed by Unlazy Investing as a specific inducement to make a particular investment or to follow a particular strategy but only as an expression of opinion.



